Search Results for: cell recognition
Cell recognition
Definition noun (1) Mutual recognition between cells, usually by specific complementary interaction between their respective... Read More
Cell membrane
Cell Membrane Definition Just like any non-living body possesses a plastic or paper packaging material that keeps the... Read More
Glycocalyx
What is the Glycocalyx? The glycocalyx is a polysaccharide-based gel-like, highly hydrous cellular thin layer, covering... Read More
Endomembrane system
Ever wondered how biomolecules are made within the cell and then they are released outside the cell for use by the body?... Read More
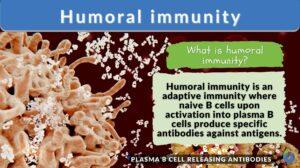
Humoral immunity
Let’s get to know where one should place humoral immunity, the topic of today’s discussion!! By the end of the article,... Read More
Endoplasmic reticulum
Endoplasmic Reticulum Definition The endoplasmic reticulum is a membrane-bound organelle in cells of eukaryotic cells... Read More
Proteoglycan
What are proteoglycans? Proteoglycans are primarily a type of polysaccharide. Structurally, proteoglycans are... Read More
Phagocytosis
Phagocytosis Definition Phagocytosis is a basic physiological cellular process wherein a cell ingests a solid particle... Read More
Cell Structure
The interior of human cells is divided into the nucleus and the cytoplasm. The nucleus is a spherical or oval-shaped... Read More
Sphingolipid
Definition noun plural: sphingolipids sphin·go·lip·id A type of lipid with a sphingoid base (e.g. sphingosine and... Read More
Oligosaccharide
Carbohydrates are organic compounds consisting of carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen, usually in the ratio of 1:2:1. They are one... Read More
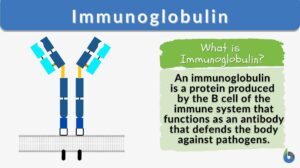
Immunoglobulin
Immunoglobulin Definition An immunoglobulin is a globulin molecule produced by the immune cells, for the body's defense... Read More
Sister chromatids
Sister Chromatids Definition Sister chromatids are defined as the two identical copies of a single replicated chromosome... Read More
Signal recognition particle
Definition noun A protein-RNA complex important in binding to the mRNA for the recognition of signal peptide on a nascent... Read More
Glycosphingolipid
Definition noun, plural: glycosphingolipids A type of glycolipid made up of a glycan (or a carbohydrate) linked to the... Read More
Cytotoxic T cell
Definition noun, plural: cytotoxic T cells A T cell responsible for inducing death to target cells (e.g. infected somatic... Read More
T-helper cell
Definition noun, plural: T-helper cells A type of T lymphocyte that assists by activating antigen-presenting leukocytes,... Read More
Glycoconjugate
Definition noun, plural: glycoconjugates A carbohydrate chemically linked to another compound, e.g. lipid or... Read More
Rough endoplasmic reticulum
Rough Endoplasmic Reticulum Definition The rough endoplasmic reticulum (rough ER or rER) is a membrane-bound organelle... Read More
Cerebroside
Definition noun, plural: cerebrosides A glycosphingolipid made of a monosaccharide or an oligosaccharide linked... Read More
Signal sequence
Definition noun A sequence of amino acid residues bound at the amino terminus of a nascent protein during protein... Read More
Amphipathic
Amphipathic Definition Amphipathic is a word used to describe a chemical compound containing both polar (water-soluble) and... Read More
Phosphorylation
Phosphorylation Definition We can define phosphorylation as a biochemical process in which a phosphate molecule is added to... Read More
Carbohydrate
Carbohydrate Definition A biomolecule refers to any molecule that is produced by living organisms. As such, most of them... Read More
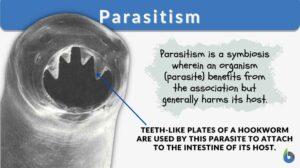
Parasitism
Organisms depend on different sources of food to survive. Larger organisms like plants make their own food (autotrophs) and... Read More
Signal peptide
Definition noun An extra-peptide extension found at the amino terminus of a nascent protein, and functions by prompting the... Read More
Nuclear body
Definition noun plural: nuclear bodies nu·cle·ar bod‧y, ˈnjuː.kli.ər ˈbɒdi Any of the prominent non-membraned,... Read More
Pathobiology of allergy and its most severe form, anaphylaxis
When allergy season looms, some people with serious hypersensitivity to allergens tend to be apprehensive of what may come.... Read More
Silent mutation
A mutation is a change in the nucleotide sequence of a gene or a chromosome. When there is only one nucleotide involved, it... Read More
Glycolipid
Definition noun, plural: glycolipids A carbohydrate, usually an oligosaccharide, that is covalently linked to a lipid... Read More
Phagolysosome
Definition noun plural: phagolysosomes (cell biology) A cytoplasmic body that forms from the fusion of phagosome and... Read More